1. Hazelcast
Hazelcast is an in-memory data grid (IMDG). In-memory data grids are distributed stores which rely primarily on the RAM for storage across a cluster for better performance. This makes IMDG’s very good caches, managing sessions across microservices, real time monitoring and so on.
An IMDG like Hazelcast, augments the core DB no matter what software it is. This reduces round trips to the the database to have better performance. This can also work as layer before APIs as well.Hazelcast is also distributed, this makes it a right fit for microservice architectures.
2. Tracing and Hazelcast and MongoDB
In previous post I explained what distributed tracing is and how to do it with Opencensus, ELK and Spring Sleuth.
To make a case why we need an IMDG like Hazelcast, I thought it be easier to to trace simple write and read requests to both Hazelcast and MongoDB.
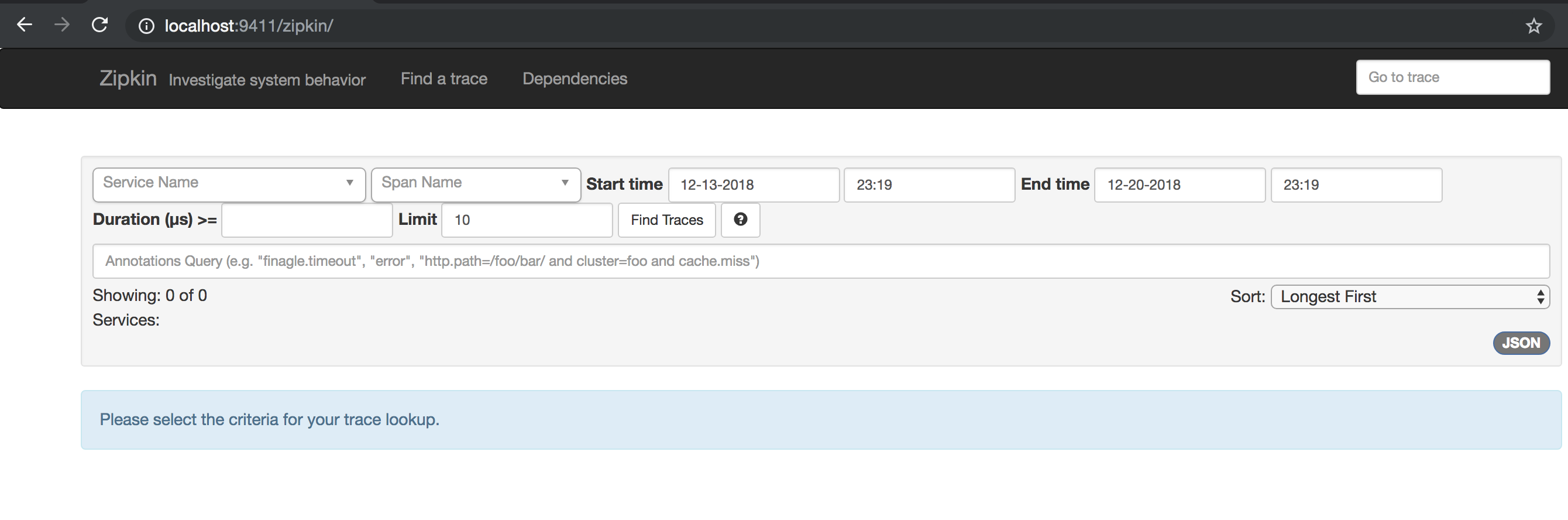
Setting up Zipkin to run on port 9411.
Now to set up a simple Spring Boot project to use Hazelcast we need to add these dependencies
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
<dependency>
<groupId>com.hazelcast</groupId>
<artifactId>hazelcast</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.hazelcast</groupId>
<artifactId>hazelcast-spring</artifactId>
</dependency>
Add our configuration file help us connect to Hazelcast.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
@Configuration
public class HazelcastConfiguration {
@Bean
public Config hazelCastConfig() {
Config config = new Config();
config.setInstanceName("hazelcast-instance")
.addMapConfig(
new MapConfig()
.setName("configuration")
.setMaxSizeConfig(
new MaxSizeConfig(200, MaxSizeConfig.MaxSizePolicy.FREE_HEAP_SIZE))
.setEvictionPolicy(EvictionPolicy.LRU) //least recently used
.setTimeToLiveSeconds(-1));
return config;
}
}
Once configured we can autowire
1
2
@Autowired
private HazelcastInstance hazelcastInstance;
and use it to write and read from Hazelcast.
Now to configure a simple spring boot mongodb app :
Now to configure our traces we simply have to add this, obviously with different names for spring.application.name so we can distinguish between the two.
1
2
3
spring.application.name=spring-cloud-hazelcast
spring.zipkin.baseUrl=http://localhost:9411
spring.sleuth.sampler.probability=1.0
and
1
2
3
spring.application.name=spring-cloud-mongodb
spring.zipkin.baseUrl=http://localhost:9411
spring.sleuth.sampler.probability=1.0
3. Comparing Hazelcast and MongoDB
We can access the write and read API for both Hazelcast and MongoDB with a simple curl request
For mongodb:
1
2
3
4
5
curl -X POST \
http://localhost:8181/mongodb/api/write/1 \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-H 'content-type: application/json' \
-d '{"type":"testing","to":"st.malike@gmail.com","idField":1}'
1
2
3
4
5
curl -X POST \
http://localhost:8181/mongodb/api/read/1 \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-H 'content-type: application/json' \
-d '{"type":"testing","to":"st.malike@gmail.com","idField":1}'
and Hazelcast
1
2
3
4
5
curl -X POST \
http://localhost:8080/hazelcast/api/write/1 \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-H 'content-type: application/json' \
-d '{"type":"testing","to":"st.malike@gmail.com","idField":1}'
1
2
3
4
5
curl -X POST \
http://localhost:8080/hazelcast/api/read/1 \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-H 'content-type: application/json' \
-d '{"type":"testing","to":"st.malike@gmail.com","idField":1}'
Now we can head over to Zipkin to verify the results.
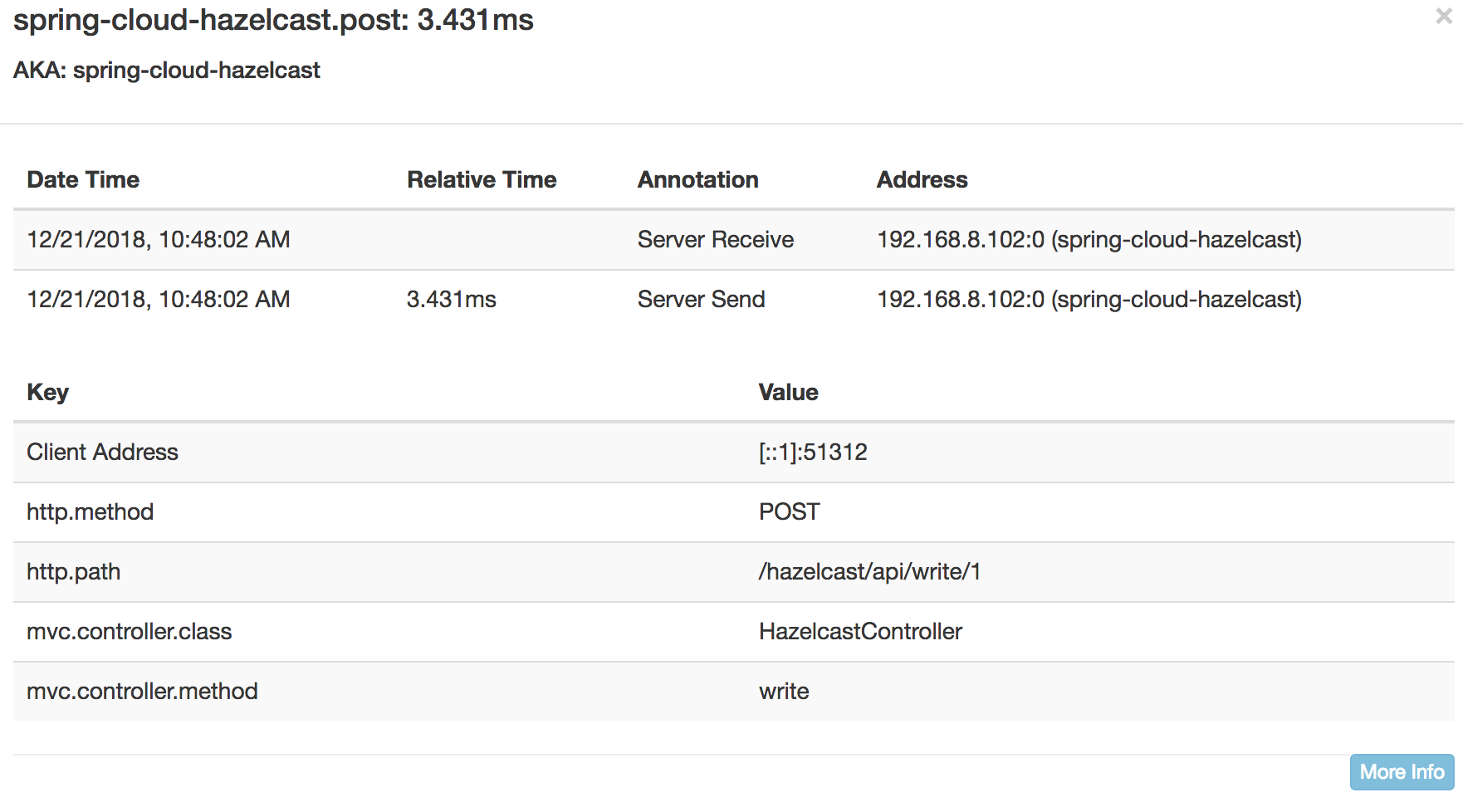
Hazelcast Write took : **3.431 ms**

MongoDB Write took : **417.952 ms**
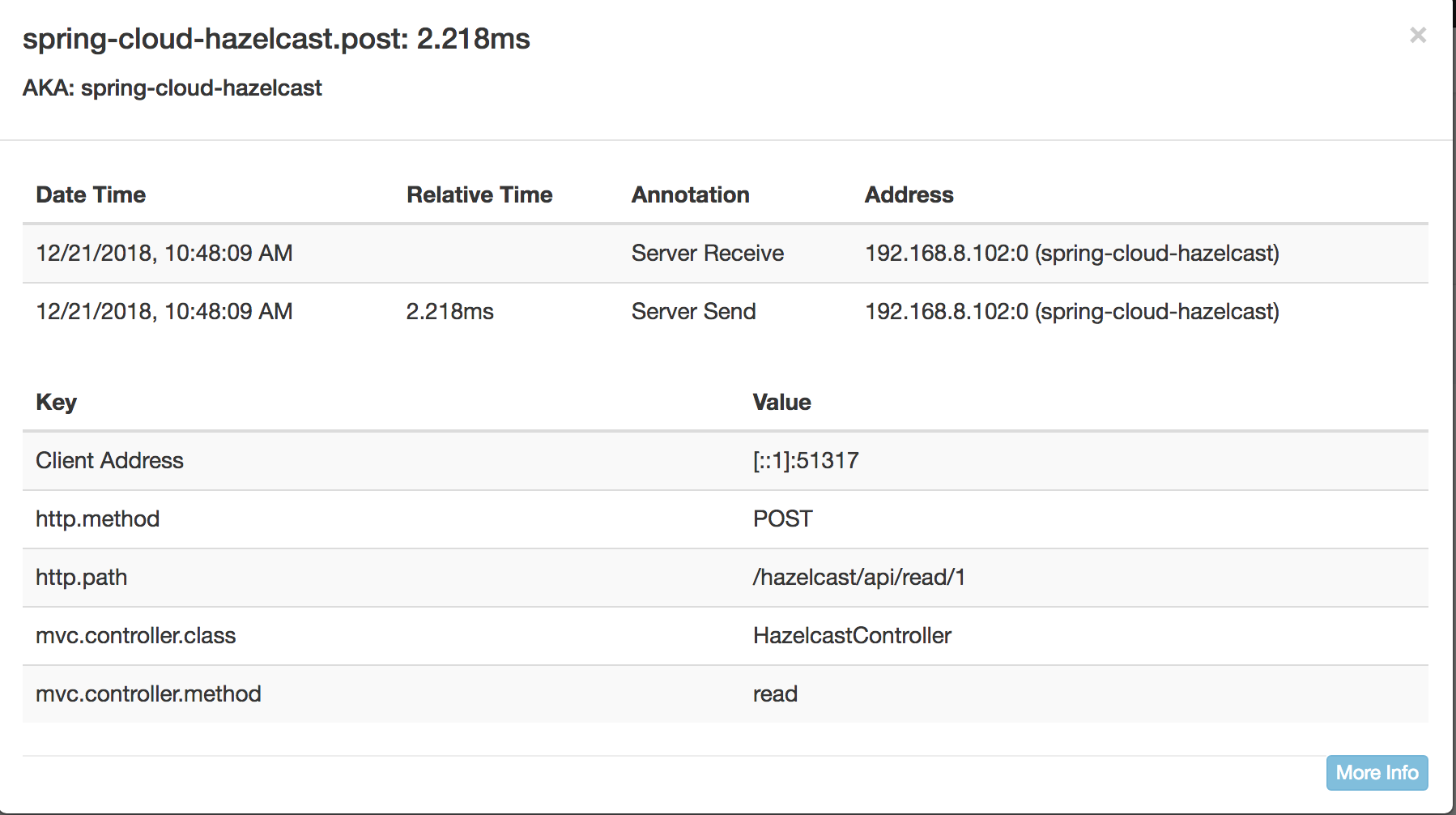
Hazelcast Read took : **2.218 ms**

MongoDB Read took : **107.486 ms**
As you can see the difference is quite clear.
4. Use Cases for Hazelcast
Caching
Hazelcast has faster reads which makes it a good candidate for a cache. This architecture requires putting Hazelcast before a database or an API with immutable response. By providing in-memory access cache data, performance of the systems designed with Hazelcast will improve significantly.
Speed Layer of Lambda Architecture and OLAP store
Hazelcast can be used as the foundation of the speed layer of a Lambda System. The speed layer computes functions over recent data with low latency and mutates your real-time data stores directly. This can be used for real time analysis due to the fact that large volumes of data can easily be accessible from an in-memory grid of data fast for real time or near real-time analysis.
This could also serve as a good store to build an OLAP unit on top of.
These are just some of the few use cases for Hazelcast, you can find other use cases here as well.
Source code also available on github
